Cupping Therapy
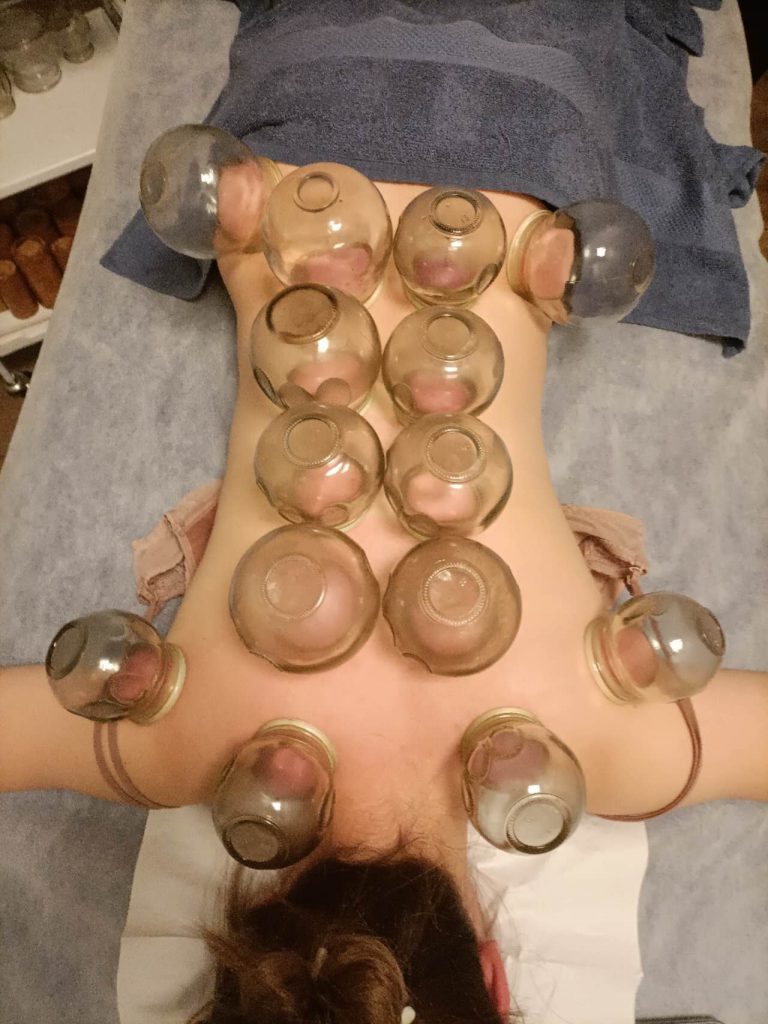
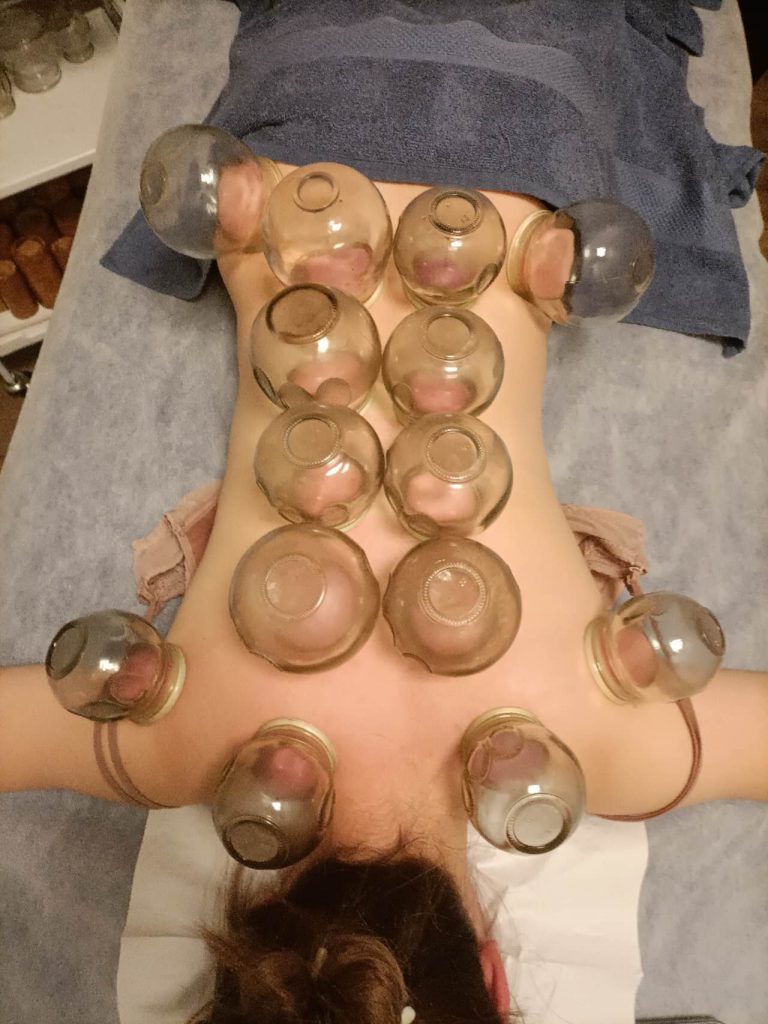
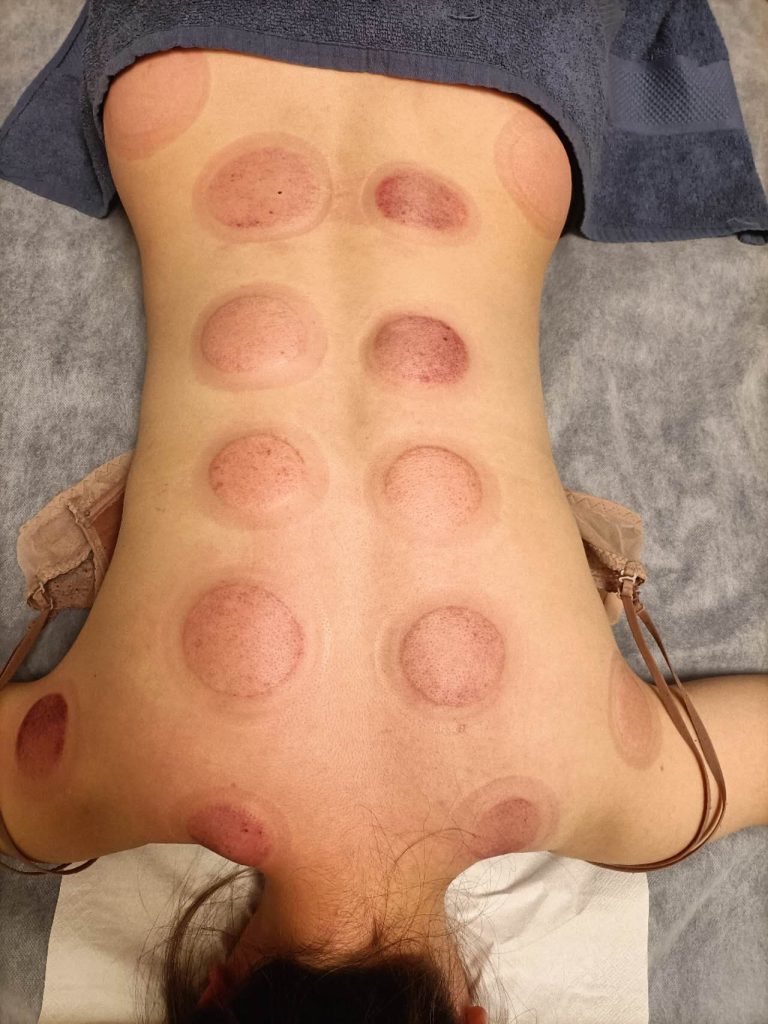
Cupping Therapy (CT) is an ancient method and currently used in the treatment of a broad range of medical conditions.
Cupping therapy effects
There is converging evidence that cupping can induce comfort and relaxation on a systemic level and the resulting increase in endogenous opioid production in the brain leads to improved pain control. Other researchers proposed that the main action of cupping therapy is to enhance the circulation of blood and to remove toxins and waste from the body. That could be achieved through improving microcirculation, promoting capillary endothelial cell repair, accelerating granulation and angiogenesis in the regional tissues, thus helping normalize the patient’s functional state and progressive muscle relaxation. Cupping also removes noxious materials from skin microcirculation and interstitial compartment which benefit the patient. Cupping may be an effective method of reducing low density lipoprotein (LDL) in men and consequently may have a preventive effect against atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Cupping is known to significantly decrease in total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein LDL/high density lipoprotein (HDL) ratio. Cupping therapy can significantly lower the number of lymphocytes in the local blood related to the affected area with an increase in the number of neutrophils, which is one of the antiviral mechanisms that reduces the pain scores. Loss of blood along with vasodilation tends to increase the parasympathetic activity and relaxes the body muscles which benefit the patient and could also be associated with the after effects of cupping. Furthermore, the loss of blood is thought to increase the quality of the remaining blood that improves pain symptoms. It has also been found that cupping increases red blood cells RBCs. It has been claimed that cupping therapy tends to drain excess fluids and toxins, loosen adhesions and revitalize connective tissue, increase blood flow to skin and muscles, stimulate the peripheral nervous system, reduce pain, controls high blood pressure and modulates the immune system.Some researchers believe that the build-up of toxins is the main reason for illness development. In the cupped region, blood vessels are dilated by the action of certain vasodilators such as adenosine, noradrenaline and histamine. Consequently, there is an increase in the circulation of blood to the ill area. This allows the immediate elimination of trapped toxins in the tissues, and, hence, the patient feels better. Cupping has been found to improve subcutaneous blood flow and to stimulate the autonomic nervous system. Like injuries to the skin due to the incisions, stimulation of the skin causes several autonomic, hormonal, and immune reactions attributed to the sympathetic and parasympathetic efferent nerves to the somato-visceral reflexes related to the organs. Cupping is reported to restore sympathovagal balance and might be cardio-protective by stimulating the peripheral sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. Cupping seems to play a role in the activation of complement system as well as modulation of cellular part of immune system. There is also a significant reduction in blood sugar in diabetic patients after cupping. Chen and colleagues concluded that there are some improvements in the research concerning the mechanisms of cupping therapy. Overall, cupping is reported to effect changes in the biomechanical properties of the skin, increase immediate pain thresholds in patients with neck pain and in a healthy subject as well, reduce significantly peripheral and local P substance and reduce the inflammation.